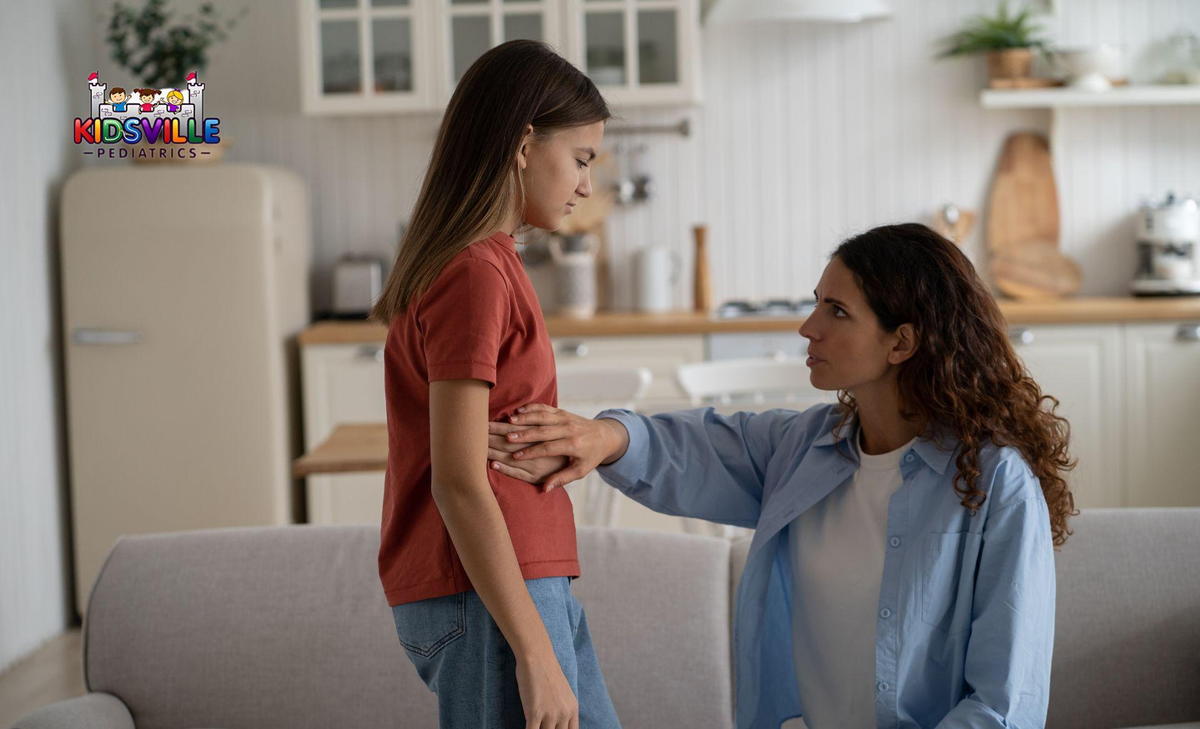
Appendicitis is a condition characterized by inflammation or infection in the appendix, a small, tube-shaped organ attached to the large intestine. The appendix is situated in the lower right part of the human abdomen. Though its exact function is not entirely understood, the appendix can become a significant medical concern if it becomes inflamed or infected. Pediatric appendicitis can escalate quickly, requiring immediate medical attention. When it strikes, it’s crucial to act promptly to ensure the health and safety of your child. At Kidsville Pediatrics McKinney, our experienced pediatricians are ready to provide the care your child needs, ensuring a swift and effective treatment process.
What Happens If Appendicitis Isn’t Treated?
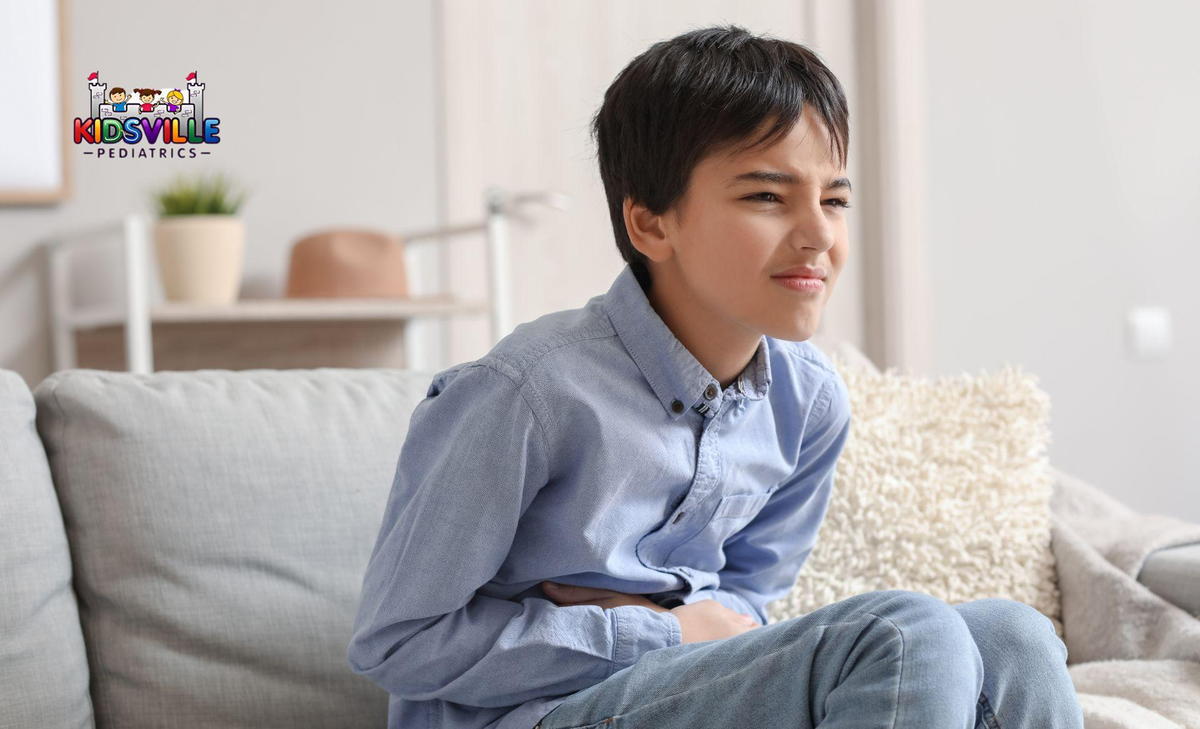

Appendicitis is a serious medical condition that should not be ignored. If left untreated, an inflamed appendix can rupture, leading to severe complications. A ruptured appendix can spread bacteria throughout the abdomen, causing a dangerous infection known as peritonitis. This infection can be life-threatening and requires emergency medical care. Additionally, bacteria from a ruptured appendix can enter the bloodstream, leading to sepsis, another life-threatening condition. Because of these risks, recognizing the symptoms of appendicitis and seeking immediate treatment is vital. Any McKinney pediatrics McKinney TX team is committed to providing prompt and effective care for children with appendicitis to prevent these severe outcomes.
How Common Is Pediatric Appendicitis?
Appendicitis is not uncommon among children and is, in fact, the most frequent cause of emergency abdominal surgery in childhood. In the United States alone, appendicitis affects approximately 70,000 children each year. It is most commonly seen in children between the ages of 10 and 19 years. While the condition can occur in younger children, it is less common in those under 10 years old. Understanding the prevalence of appendicitis and being aware of its symptoms can help parents take swift action when needed.
Symptoms and Causes of Appendicitis in Children
What Causes Appendicitis in Children?
The exact cause of appendicitis is not always clear, but it is most often due to an obstruction or blockage at the opening of the appendix. This blockage can result from various factors, including:
Abdominal infections that spread to the appendix.
Infections in the digestive tract.
Stool, parasites, or growths inside the appendix.
These blockages lead to inflammation, and if left untreated, they can cause the appendix to become infected and possibly rupture.
What Are the Symptoms of Pediatric Appendicitis?
Recognizing the symptoms of pediatric appendicitis is critical for ensuring your child receives timely medical care. One of the hallmark signs of appendicitis is abdominal pain, particularly in the lower right side of the abdomen. This pain often begins around the belly button and gradually moves to the lower right side as the condition progresses. Other symptoms to watch for include:
Nausea and vomiting.
Loss of appetite.
Low-grade fever.
If your child exhibits these symptoms, especially if the abdominal pain intensifies over time, it’s essential to seek medical attention immediately.
Diagnosis and Tests
How Is Appendicitis in Children Diagnosed?
When you bring your child to the McKinney pediatrics doctors with symptoms of appendicitis, a thorough evaluation will be conducted. The diagnosis process typically includes a physical exam, during which the healthcare provider will press on the abdomen to check for tenderness, pain, or swelling. Additionally, the pediatricians will ask about your child’s symptoms and medical history to gather more information.
To confirm the diagnosis, your child’s pediatrician may order blood and urine tests to check for signs of infection. Imaging tests are also commonly used to get a clearer view of the appendix and surrounding structures.
What Types of Imaging Tests Might Be Used?
To accurately diagnose appendicitis, the following imaging tests may be used:
Abdominal X-ray: Provides a basic image of the abdomen to check for abnormalities.
Abdominal Ultrasound: Uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the internal organs, including the appendix.
Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: Offers detailed cross-sectional images of the abdomen using a combination of X-rays and computer technology.
These imaging tests help healthcare providers determine whether the appendix is inflamed and the best course of action for treatment.
Management and Treatment of Appendicitis
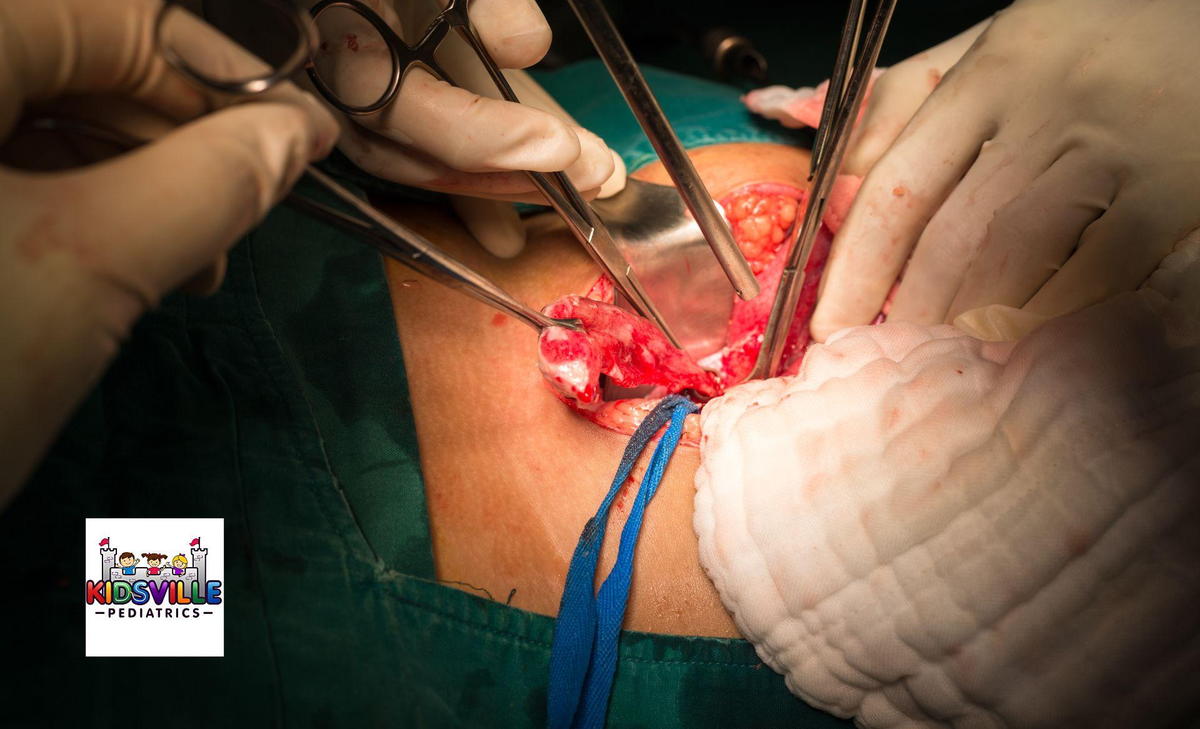
The treatment for appendicitis in children typically involves surgery to remove the appendix, known as an appendectomy. In some cases, if the appendicitis is detected early, antibiotics alone may be sufficient to treat the condition. However, surgery is the most common and effective treatment method, especially in more severe cases.
Types of Appendectomy
There are two primary methods for performing an appendectomy:
Laparoscopic Appendectomy: In this minimally invasive procedure, the surgeon makes several small incisions in the lower right abdomen. A video camera is inserted through one of the incisions to guide the surgeon, who then uses specialized instruments to remove the appendix. This method generally results in a shorter recovery time and lower risk of infection.
Laparotomy (Open Surgery): This method involves making a larger incision in the lower right abdomen to remove the appendix. Laparotomy is typically used in more complicated cases, such as when the appendix has already ruptured. The recovery time for this surgery is longer compared to laparoscopic surgery.
Before the surgery, your child will receive antibiotics to reduce the risk of infection. A pediatric anesthesiologist will administer anesthesia to ensure your child is asleep and comfortable during the procedure. The surgery itself usually takes about an hour.
What Happens After Surgery?
The recovery process after an appendectomy depends on the severity of the appendicitis. For uncomplicated cases, where the appendix is removed before it ruptures, most children can go home the day after surgery or even the same day. However, if the appendix has ruptured, leading to more severe infection, your child may need to stay in the hospital for about five days to receive intravenous (IV) antibiotics.
During the hospital stay, your child will also receive IV pain medication to manage discomfort. Once your child can eat a regular diet, has no fever, and the incision site is healing well, they will be discharged from the hospital.
Post-Surgery Care and Potential Complications
What Complications May Arise After Surgery for Appendicitis?
While most children recover without issues after an appendectomy, complications can sometimes occur, particularly in cases of ruptured appendicitis. Some of the potential complications include:
Infections: The surgical site or the abdominal cavity may develop infections, which can usually be treated with antibiotics. In some cases, the wound may need to be reopened and cleaned.
Abscesses: These are pockets of pus that can form in the abdomen. Smaller abscesses may be treated with antibiotics, while larger ones may require drainage.
Small Bowel Obstructions: A partial or complete blockage of the small intestine can occur after surgery, sometimes requiring additional surgery to resolve.
If you notice any signs of complications, such as fever, increasing pain, vomiting, or excessive swelling, redness, or drainage from the incision site, contact your child’s healthcare provider immediately.
Outlook and Recovery
How Soon After Treatment Will My Child Feel Better?
Most children recover quickly after an appendectomy. There are no significant dietary or lifestyle restrictions needed post-surgery. However, it’s important to monitor your child’s physical activity during the recovery period. Children who undergo laparoscopic surgery should limit physical activity for the first three to five days, while those who had open surgery (laparotomy) should rest for about 10 to 14 days before resuming regular activities.
Follow-Up Care and Monitoring
When Should I Take My Child to a McKinney Doctor?
A follow-up visit will typically be scheduled two to four weeks after surgery. During this visit, the healthcare provider will examine the surgical wound, assess your child’s recovery, and answer any questions you may have. Minor swelling around the incision site is normal, but if you notice any signs of infection or other concerns, don’t hesitate to reach out to your child’s healthcare provider.
Key Questions to Ask Your Child’s McKinney Pediatrician
If your child is diagnosed with appendicitis, consider asking the healthcare provider the following questions:
What type of appendectomy surgery is best for my child?
When can my child return to school and regular activities?
How can I differentiate between appendicitis and other common stomach issues in my child?
At Kidsville Pediatrics McKinney, our priority is your child’s health and well-being. We are here to guide you through every step of the pediatric appendicitis diagnosis and treatment process, ensuring the best possible care for your child.
You may schedule an appointment online: https://www.kidsvillepeds.com/appointment/ Or visit/call our clinics: Kidsville Pediatrics Mansfield TX: 682-341-3910; 1759 Broad Park Circle S, Suite 201 & 205, Mansfield, TX Kidsville Pediatrics Southlake: 682-345-8010; 2813 W. Southlake Blvd Suite 100 Southlake, TX Kidsville Pediatrics McKinney: 469-885-9400; 5881 Virginia Pkwy. Suite 300 Mckinney, TX |